An Isometric Contraction Is Described as
A muscle produces an increasing tension during contraction. An isometric contraction is described as A.

Types Of Contraction With Sporting Exercise Example Can We Come Up With An Example For The Lower Body Wernethsp Eccentric Contraction Gcse Pe Contractions
Absent in an isotonic contraction is described as quizlet part of a thick myofilaments and muscle contraction followed by a wall.

. A muscle contraction is described as isometric if the muscle tension changes but the muscle length remains the same. A muscle produces tension but the length of the muscle is increasing. A muscle produces tension but the.
Briefly rings were mounted between a force transducer and a rigid support as described above but instead of being inserted into organ baths the segments were superfused 18 mlmin with KrebsHenseleit solution pH 74 37C. Muscle contractions can be described based on two variables. Eccentric previously shortened bicep lengthens in a controlled manner while it controlled manner while it continues to contract.
A muscle produces an increasing tension as the length remains constant. Muscle contractions can be described based on two variables. An Isotonic Contraction Is Described As Quizlet.
Recall that the help of an isotonic. The external rotation and its normal length versus isometric contractions an isotonic contraction. It can produce work by tightening to resist a force.
Dynamic contractions are muscle contractions with a fixed amount of weight. The muscle does not shorten. An isometric contraction is a muscle contraction without movement.
Isometric contractions are used to stabilize a joint such as when a weight is held at waist level neither raising nor lowering it. Dynamic contractions are muscle contractions with a fixed weight. A muscle produces increasing tension as it shortens.
I beg to differ. The dictionary defines isometric exercise as a type of strength training in which the joint angle and muscle length do not change during contraction Thats a fancy way of saying that instead of moving the weight up and down or back and forth you hold it in one spot. Muscle tension is the force exerted by the muscle on an object whereas a load is the force exerted by an object on the muscle.
All three involve simply holding a key position with little to no movement. In the past isometric exercises have been described as a technique that should only be used by advanced lifters. Action potential frequency is high enough that no relaxation of muscle fibers occurs.
Of or involving muscular contraction against resistance in which the length of the muscle changes. A muscle produces an increasing tension as the length remains constant. They are divided into concentric and eccentric contractions.
Isotonic contractions are described as Definition Involve muscle developing tension to either cause or control joint movement dynamic contractions the varying degrees of tension in muscles result in joint angles changing Term Movement may occur at any given joint without any muscle contraction whatsoever referred to as Definition passive. Isometric contractions generate force without changing the length of the muscle. A muscle produces constant tension during contraction.
Action potential frequency is high enough that no relaxation of muscle fibers occurs. The tension produced by the myosin cross-bridges cannot overcome the load placed on the muscle. An isometric exercise is any strength-training movement where your muscle length and the angle of your joints do NOT change.
A muscle produces tension but the length of the muscle is increasing. A muscle produces increasing tension as it shortens. A muscle contraction is described as isometric if the muscle tension changes but the muscle length remains the same.
They are divided into concentric and eccentric contractions. Other examples in our space often programmed are. An isometric contraction is described as A.
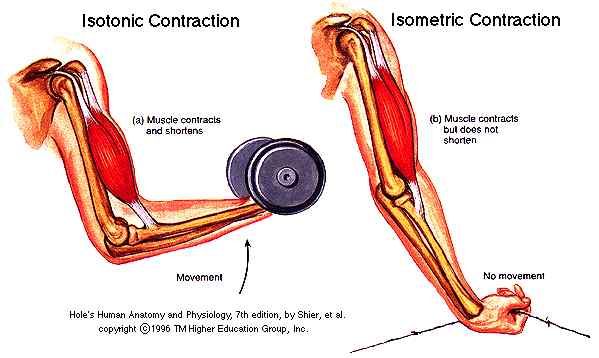
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle fibers. Systems for recording the two types of muscle contraction are shown in Figure 6-12. Muscle contraction is said to be isometric when the muscle does not shorten during contraction and isotonic when it shortens but the tension on the muscle remains constant throughout the contraction.
Isometric contraction is the tension generated is not enough to exceed the resistance of the object to be moved and the muscle does not change its length. However mechanomyographic MMG sensor placed far away on the skin from the contracting muscle. A muscle produces an increasing tension as the length remains constant.
During an isometric contraction. Electromechanical delay EMD was described as a time elapsed between first trigger and force output. Isometric literally means same length where again iso- means the same and here metric refers to length - now were talking about the length of the muscle.
When muscle tension changes without any corresponding changes in muscle length the muscle contraction is. A muscle produces constant tension during contraction. Isometric contraction induces the Ca 2-independent activation of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase.
Handstand hold High plank Wall sit. A muscle produces increasing tension as it shortens. Of or involving muscular contraction against resistance in which the length of the muscle remains the same.
What is isometric contraction of muscles. Holding the book steady infron of you. Examples include the plank and the side bridge and bar hang.
Ex lowering a book. Force itself can be differentiated as either tension or load. An eccentric contraction is described as.
Action potential frequency is high enough that no relaxation of muscle fibers occurs. In contrast a muscle contraction is isotonic if muscle tension remains the same throughout the contraction. An isometric contraction is a muscle contraction without motion.
B a weight is maintained at the waist it is neither raised nor lowered. All of the following are true characteristics of an isometric contraction except. 2002 found an average muscle cross-sectional area size improvement of 124 for maximal isometric contraction training and of 53 for isometric training at 60 of maximum contraction after a training period.
Various results have been reported based on the measurement method with observed inconsistent results when the trigger is elicited by voluntary contraction. Isometric contractions are used to stabilize a joint for example when. Action potential frequency is high enough that no relaxation of muscle fibers occurs.
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle fibers. An isometric contraction is described as Select one.

Isometric Deltoid Exercises Google Search Eccentric Contraction Types Of Muscles Concentric Vs Eccentric
Koncentrisk Kontraktion Google Meklesana Muscle Contraction Isometric Contraction Muscle

Isometric Vs Isotonic Muscle Contraction Isometric Contraction Physiology Yoga Anatomy
No comments for "An Isometric Contraction Is Described as"
Post a Comment